To stay competitive, many organizations must revolutionize production procedures. RFID technology can boost production productivity and precision. RFID tags and readers allow manufacturers to track processes and data autonomously in real-time, giving unequaled precision and insight.
Increased accuracy boost production, minimizes waste, and makes customers happier by delivering orders quickly and accurately. RFID technology may alter firms by improving inventory management, supply chain management, and quality control.
In this article, we’ll examine how
RFID Technology: An Overview
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) uses radio waves to convey data about specified objects. It uses tags and electromagnetic induction. These antenna-and-chip tags can be attached or inserted in cards, animals, and other products.
The tag’s antenna receives radio waves from a reader, and the chip returns the object’s unique identifying number.
RFID tags can be used in manufacturing, retail, and healthcare due to their small size and ability to stick to practically any surface.
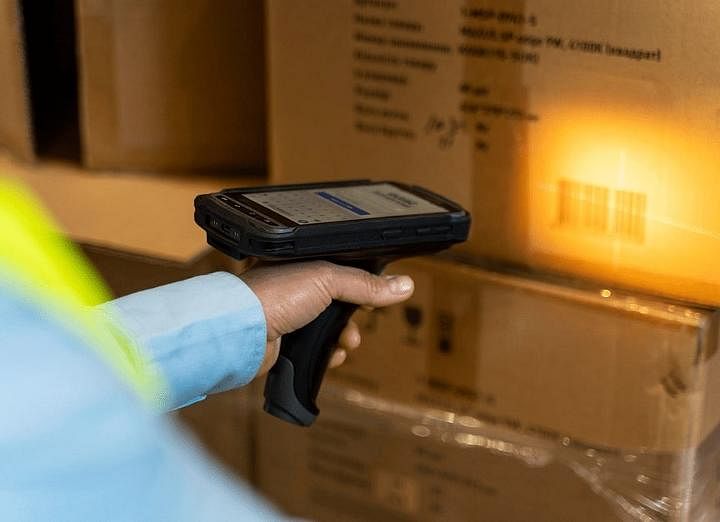

How Does The RFID System Work For Manufacturing?
Manufacturers can track and trace their items in real-time with it. Implementing RFID technology for production requires attaching RFID tags to things, deploying RFID readers, and integrating RFID data with existing systems.
Manufacturers may streamline operations, enhance accuracy, decrease waste, and boost output using these methods. Due to its many benefits, RFID in manufacturing has become more prevalent and helps organizations stay competitive in the ever-changing sector.
Identifying Products and Ensuring Tag Durability
Preparing and identifying products or objects to track before using RFID in manufacturing is crucial. This stage will determine the system’s readers and tags. The RFID tags must also endure the manufacturing environment and any extreme conditions.
If the manufacturing process involves intense temperatures, choosing tags that can survive them is crucial. The system will deliver accurate data with proper planning, RFID tag, and reader selection.
Manufacturers can successfully adopt RFID technology and get production insights by addressing these variables.
Tag Attachment and Embedding
The goods or things being monitored must have the correct RFID tag attached or insert. The attaching or embedding process determines whether the system uses an active or passive tag. Passive tags use energy from a reader, while active tags need wiring.
To be identified by a reader device, each tag must have a unique code. The tag’s functionality and data accuracy depends on how it’s attached or embedded.
Manufacturers can guarantee their RFID system works well and delivers significant insights into their production processes by properly attaching or inserting tags.
Installing RFID Readers for Seamless Tracking
After choosing and attaching RFID tags, install the right reader at each production line stage. These readers retrieve information from adjacent RFID tags. To ensure manufacturing ERP connection, numerous readers should be correctly connected.
RFID reader placement should enhance coverage and accuracy. To ensure reliable data gathering, readers should be calibrated and tested. The RFID system’s production process insights depend on reader installation and calibration.
Manufacturers can maximize RFID implementation and production by installing and maintaining readers.
Data Management
RFID readers collect data and send it to an information system for storage and analysis. Data can inform production process optimization and cost reduction programs. Managed and analyzed data to ensure accuracy and meaning.
The information system should store and manage enormous volumes of data and enable real-time manufacturing process visibility. Advanced analytics technologies can process the data and provide insights for informed decision-making.
Effective RFID implementation in manufacturing requires data management and analysis to help manufacturers make informed decisions that boost efficiency and production.
Advantages of Implementing RFID Technology in the Manufacturing Industry
Manufacturers can track and trace their items in real-time with RFID. It provides a variety of advantages that can make production and supply chain processes brisker, less difficult, and safer to carry out.
The following is a list of some of the advantages of RFID in manufacturing:
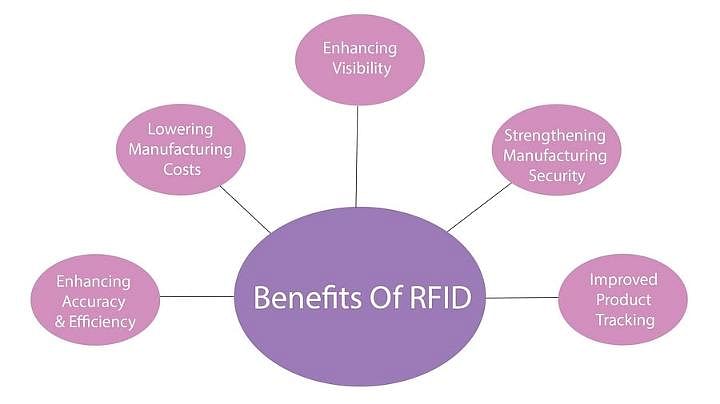
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency
RFID technology automates data collecting and reduces data entry errors in manufacturing. RFID tags reduce manual scanning and data entry, speeding and improving manufacturing ERP data processing.
It also allows firms to identify and fix production inefficiencies swiftly. Reduced downtime, mistakes, and productivity optimize efficiency. It can improve inventory accuracy and reduce laborious inventory counts.
RFID technology can help manufacturers compete in a fast-changing industry by improving accuracy and efficiency.
Lowering Manufacturing Costs
RFID inventory solution reduces labor and inventory expenses for manufacturers. Data collecting and tracking automation can reduce human labor and save money over time. RFID improves inventory visibility and tracking, lowering inventory management expenses.
This can enhance warehouse efficiency and inventory accuracy, lowering expenses. RFID technology helps manufacturers boost profits and reinvest by reducing labor and inventory costs. RFID technology’s precision and efficiency can increase consumer satisfaction and the manufacturer’s bottom line.
Enhancing Visibility
Manufacturers can spot issues in real-time with RFID technology. Manufacturers can gain insights into performance, quality control, and compliance by accessing real-time production data. This improves decision-making by allowing proactive problem-solving before difficulties become significant.
RFID technology improves supply chain visibility and control, helping firms plan and execute production operations. Resource efficiency and performance can improve.
RFID technology’s increased visibility gives manufacturers a significant tool to improve their operations’ accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness, leading to better outcomes and decision-making.
Strengthening Manufacturing Security
RFID security improves manufacturer security. Each RFID tag or card can enter limited locations, increasing protection against fraudulent or illegal access. Tracking and identifying goods across the supply chain can deter theft and counterfeiting.
RFID tags can be programmed to alarm if moved outside permitted regions or removed without permission. RFID systems can also record who has accessed specific locations or products for compliance and security.
RFID technology prevents unwanted access and tracks item movement across the supply chain, improving production security.
Improved Product Tracking
RFID improves manufacturer tracking. RFID systems enable real-time supply chain monitoring by tracking products from order fulfillment to delivery. They can immediately spot bottlenecks and delays, allowing for swift fixes that boost productivity.
RFID technology can also prevent lost or stolen objects. Manufacturers can receive warnings when tagged items are moved or tampered with. This feature protects products and gives customers peace of mind.
Selecting the Optimal RFID Tag for Enhanced Manufacturing Operations
Understanding all of the relevant aspects and choosing RFID tags that are the best fit for your industrial operations are the two most essential steps in making the right choice. When making this decision, these are some of the most important factors to take into consideration:
Material Selection
Choose the proper RFID tag material for maximum performance. Chemical, moisture, and extreme temperature resistance make epoxy-resistant tags appropriate for tricky situations. Polyester and vinyl tags are cheaper for one-time usage.
Consider the operational environment and product type when choosing an RFID tag. If the product is metallic or contains a lot of metal, a tag with a bigger antenna may improve signal transmission. Long-range tags demand higher-powered readers, which may increase system costs.
Frequency Range
RFID systems’ frequency ranges affect their performance in diverse situations. LF RFID tags are utilized for short-range applications like access control, while HF tags are used for data transfer over slightly longer distances like inventory management or asset tracking using RFID.
UHF tags are suitable for supply chain management but more prone to interference. When picking an RFID frequency range, consider the surroundings and distance.
Tag Size and Shape
When picking an RFID tag for manufacturing, size and shape matter. The tag size and shape may need to be adjusted for the things being tracked. If the tracked objects are small, the tags may need to be smaller to attach or embed without affecting their usefulness.
Some manufacturers customize tags to meet the application. To integrate tag size and form into manufacturing, plan ahead.
Consideration of Cost
Cost is crucial when picking RFID tags for production. Tags and materials vary in price, and installation and upkeep may be extra. For the best system, the budget must be set and monies allocated.
Remember that more expensive tags may offer superior features or durability, but balancing cost and usefulness is crucial to get the best value.
It may also be good to evaluate rates from multiple suppliers and consider long-term savings in efficiency, accuracy, and inventory management.
Consider Special Features & Functions
Consider specific RFID tags for production. To maintain quality, perishable products may require temperature monitoring.
Extended read ranges benefit more extensive product lines and warehouses. To improve RFID tag performance for your use case, determine what features and functions are necessary.
By considering these factors, manufacturers can use RFID technology to streamline, cut costs, and boost productivity.
Selecting the Optimal RFID Tag for Enhanced Manufacturing Operations
Understanding all of the relevant aspects and choosing RFID tags that are the best fit for your industrial operations are the two most essential steps in making the right choice. When making this decision, these are some of the most important factors to take into consideration:
Material Selection
Choose the proper RFID tag material for maximum performance. Chemical, moisture, and extreme temperature resistance make epoxy-resistant tags appropriate for tricky situations. Polyester and vinyl tags are cheaper for one-time usage.
Consider the operational environment and product type when choosing an RFID tag. If the product is metallic or contains a lot of metal, a tag with a bigger antenna may improve signal transmission. Long-range tags demand higher-powered readers, which may increase system costs.
Frequency Range
RFID systems’ frequency ranges affect their performance in diverse situations. LF RFID tags are utilized for short-range applications like access control, while HF tags are used for data transfer over slightly longer distances like inventory management or asset tracking using RFID.
UHF tags are suitable for supply chain management but more prone to interference. When picking an RFID frequency range, consider the surroundings and distance.
Tag Size and Shape
When picking an RFID tag for manufacturing, size and shape matter. The tag size and shape may need to be adjusted for the things being tracked. If the tracked objects are small, the tags may need to be smaller to attach or embed without affecting their usefulness.
Some manufacturers customize tags to meet the application. To integrate tag size and form into manufacturing, plan ahead.
Consideration of Cost
Cost is crucial when picking RFID tags for production. Tags and materials vary in price, and installation and upkeep may be extra. For the best system, the budget must be set and monies allocated.
Remember that more expensive tags may offer superior features or durability, but balancing cost and usefulness is crucial to get the best value.
It may also be good to evaluate rates from multiple suppliers and consider long-term savings in efficiency, accuracy, and inventory management.
Consider Special Features & Functions
Consider specific RFID tags for production. To maintain quality, perishable products may require temperature monitoring.
Extended read ranges benefit more extensive product lines and warehouses. To improve RFID tag performance for your use case, determine what features and functions are necessary.
By considering these factors, manufacturers can use RFID technology to streamline, cut costs, and boost productivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RFID technology has had a significant impact on production. It improves accuracy, efficiency, visibility, security, and tracking. Automating data gathering and monitoring allows producers to spot errors before they become significant problems.
Manufacturers can optimize their operations with real-time manufacturing data. Customers obtain their products on time and in good shape by tracking products from order fulfillment to delivery.
Consider materials, frequency, size, and cost when choosing RFID tags for manufacturing. RFID use in manufacturing is predicted to increase as technology advances, improving efficiency, quality, and customer happiness.

| About Author
Rajesh R
A seasoned IT Integrations and ERP Solution Architect boasts over a decade's expertise in revolutionizing business processes through cloud-based ERP and MIS software solutions. Proficient in leveraging avant-garde technologies such as Blockchain, Al, IoT, etc in crafting bespoke software solutions. His extensive background encompasses tailor-made software solutions across diverse industries like Sales, Manufacturing, Food Processing, Warehouse Operations→ and B2B Businesses. Rajesh excels in engineering and deploying enterprise-grade business software, playing a pivotal role in Business Solution Consulting and designing intricate software solution architectures for many Fortune 500 enterprises.
Schedule Consultation with Rajesh Schedule Now